Adgarion for Coligny Calendar Rites
Coligny Calendar-Based Daily Rituals
Amidst various cultural practices, one custom is the concept of daily offerings. These offerings are typically small and are accompanied by humble prayers or invocations. Engaging in these rituals serves the purpose of ingraining piety as a habitual practice.
Excellence, then, being of these two kinds, intellectual and moral, intellectual excellence owes its birth and growth mainly to instruction, and so requires time and experience, while moral excellence is the result of habit or custom.
Aristotle, ‘Nicomachean Ethics, Book II’
While it wouldn’t be accurate to claim that we derived our idea solely from this quote, it aligns well with our concept and is agreeable. When we turn our (Îanoi) virtues into habits, we are more likely to adhere to them. This is significant as it reflects our commitment to being responsible community members and true to ourselves. Moreover, these actions are pleasing to the Dêuoi we worship. To cultivate the virtue of dêuocariâ (piety) as a habit, we devised a practical system. This approach serves as a means to enhance our connections with the Dêuoi and fortify our adherence to Bessus (customs) along with taking part in Cantos Roti (gifting cycle) which fosters Sumatreiâ (Good Relationship). We pondered, “What kind of daily ritual setup would have been logical for a member of our Toutâ?”
In this pursuit, we turned to the most renowned piece of Gaulish timekeeping — the Coligny Calendar. Drawing inspiration from it, we formulated a methodology for daily adaððoues (rituals). Our intention was to keep the structure straightforward, and coincidentally, it aids in remembering the current Coligny Calendar date.
For members of Bessus Nouiogalation (BNG), consistent adherence is only obligatory for those in the Delgaunos tier. Nevertheless, it is encouraged for Toution to make an attempt. This framework applies to all months, with one distinction between 29 and 30-day months. Given that this is a BNG arrangement, it should be unsurprising that each of our Toutâdeuoi (deities of a group) are represented with a day each.
A simple offering suffices for these daily rituals. A suggested item to consider offering is incense, as it is readily accessible, cost-effective, and generally well-regarded as a suitable offering. Another recommendation is to integrate these adaððoues (rituals) into your everyday schedule. Align them with your waking moments, before sleep, or after bathing. Associating them with other daily activities is notably beneficial.
Common Questions
What about Bituatîs (land beings)?
Generally, these adaððoues (rites) are done indoors. Though indeed it could be possible to offer to them indoors, it is generally encouraged to meet them in their domains. This, and taking into account that the Gauls knew of cooler winters, and many places of very cold ones. As such, we didn’t want to put it on anyone to make such a trip in inclement weather when it may be unsafe.
What if one wishes to do more than the amount of offerings in the structure? Or gives worship to more Dêuoi than the structure accommodates?
It’s worth mentioning that what we’ve done here is merely provide a baseline. One can always do more. Those who do undoubtedly will easily be able to figure out a pattern that works for them. Whether it be multiple adaððoues in the same day, or simply offering to different Dêuoi on the open day. On the last open day of the seven day structure, one doesn’t have to stick to the same Dêuoi every week. It could be different Dêuoi each time. The free spot allows for either a set-aside space for devotional relations or a chance to build new relationships.
The Breakdown
We use our Coligny Calendar app
From the beginning of the month, our structure is as follows:
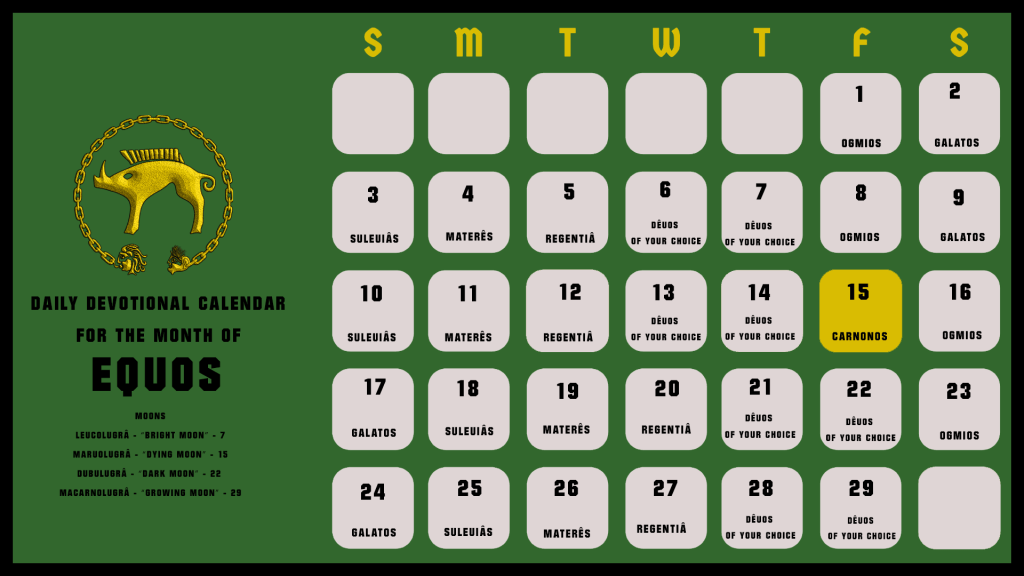
Each First Quarter moon, we will have a new Calendar for you all.
- 1 – Ogmios (Ancestor of the Gauls)
- 2 – Toutatis (Guardian of the Toutâ)
- 3 – Suleuiâs (Good Guides)
- 4 – Materês (Knowers of fate, life givers)
- 5 – Regentiâ (Ancestors)
- 6 – Celtînâ (Mother of Virtue)
- 7 – A “Dêuos of your choice”, or none. Though the former is strongly recommended. Also useful if there is a previous day that one missed. The free spot allows for either a set-aside space for devotional relations or a chance to build new relationships.
This cycle repeats for days 8-14. Thus, we arrive at the middle of the month.
- 15 – Carnonos (Way opener, guardian between worlds)
After which, the cycle of the first 14 days repeats. Which covers days 16-29.
- 30 – Carnonos (Way opener, guardian between worlds)
Carnonos will only show up again in a month with 30 days.
30-day months are marked matis (good, favorable)
29-day months are marked anmatis (bad, unfavorable)
May the Dêuoi look favorably upon the attempt, and may they give blessings to you all.
Adgarion for Coligny Calendar Rites
You can find the format of our rites HERE
Ogmios
Diioi I, VIII, XVI, XXIII
Days, 1, 8, 16, 23
Adgarion Ogmiû
Adgariomos/Adgariūmī Ogmion
Cintuatîr Galation
Mârolabâtis
Belolatis
Excenu bebanastû, uxelliâ Galation, rodîssestûnis anuan anson
Rodîmos/Rodîumî adbertâ etic bratûn tê
Addatus
Arcimâs
Slanon te
Bratûn te
Molâmos/Molâmî Ogmiû
Iâmos/Iâiumî in tancê
Invocation for Ogmios
We/I invoke Ogmios
First father of the Galatîs
Great speaker
Mighty hero
From far you came, pride of the Galatîs, you gave us our name
We/I give offering and thanks to you
Offering
Requests
Cheer to you
Thanks to you
We/I praise you Ogmios
We/I go in peace

Back to table of contents
Galatos
Diioi II, IX, XVII, XXIV
Days, 2, 9, 17, 24
Adgarion Galatû Toutatî
Adgariomos/Adgariūmī Toutaton
Latis Toutiâs
Nertos urittosergios
Uernos Anson
Anegestûnis etic rodîestû tancon
Rodâmos/Rodâmî addatus etic bratun tê
Addatus
Arcimâs
Slanon te
Bratûn te
Molâmos/Molâmî Galatû Toutatî
Iâmos/Iâiumî in tancê
Invocation for the Toutais Galatos
We invoke the Toutatis Galatos
Hero of the people
Mighty against disease
Our guardian
You protect us and give us peace
We give offering and thanks to you
Offering
Requests
Cheer to you
Thanks to you
We/I praise you Toutatis Galatos
We/I go in peace

Back to table of contents
Suleuiâs
Diioi III, X, XVIII, XXV
Days, 3, 10, 18, 25
Adgarion Suleuiâbo
Adgariomos/Adgariūmī Suleuiâs
Uernâs uissoues
Delgaunâs rextuon
Carâs uîrisamâs
Esue leucos îani uedetesuîs ollon
Rodâmos/Rodâmî addatus etic braton suos
Addatus
Arcimâs
Slanon te
Bratûn te
Molâmos/Molâmî Suleuiâbo
Iâmos/Iâiumî in tancê
Invocation for the Suleuiâs
We/I invoke the Suleuiâs
Wise guardians
Keepers of right
Truest friends
You all are the light of virtue, you guide us all
We/I give offering and thanks to you all
Offering
Requests
Cheer to you
Thanks to you
We/I praise you Suleuiâs
We/I go in peace

Back to table of contents
Materês
Diioi IV, XI, XIX, XVI
Days, 4, 11, 19, 26
Adgarion Materebo
Adgariomos/Adgariūmī Materês
Biuotus rodamaunâs
Caddos maiamos
Uissuaunâs tonceton
In geni, biuê, etic maruê, uednis etic messus ollon
Rodâmos/Rodâmî addatus etic bratun suos
Addatus
Arcimâs
Slanon te
Bratûn te
Molâmos/Molâmî Materebo
Iâmos/Iâiumî in tancê
Invocation for the Materês
We/I invoke the Materês
Life givers
Most holy
Knowers of fates
In birth, life, and death, guiding and measuring us all
We/I give offering and thanks to you all
Offering
Requests
Cheer to you
Thanks to you
We/I praise you Materês
We/I go in peace
Back to table of contents
Regentiâ
Diioi V, XII, XX, XVII
Days, 5, 12, 20 ,27
Adgarion Regentiobo
Adgariomos/Adgariūmī Regentiâ
Senomaterês etic Senaterês
Senoueniâs
Regentiâ coimâs
Rodissatesuîs biuotus nîs etic uilietesuîs snî
Rodâmos/Rodâmî addatus etic bratun tê
Addatus
Arcimâs
Slanon te
Bratûn te
Molâmos/Molâmî Regentiobo
Iâmos/Iâiumî in tancê
Invocation for the Regentiâ
We/I invoke the Ancestors
Old mothers and old fathers
Old families
Dear Ancestors
You gave us life and you watch [over] us
We/I give offering and thanks to you
Offering
Requests
Cheer to you
Thanks to you
We/I praise you Regentiâ
We/I go in peace

Back to table of contents
Celtînâ
Diioi VI, XIII, XXI, XXVIII
Days 6, 13, 21, 28
Adgarion Celtînî
Adgariomos/Adgariūmī Celtînan
Cintumatir Galation
Cintus in nertê etic canî
Druticos in ollontobi
Matirmarâ Galation, uxelliâ aisson, ton boudiâ enatâssetnis
Rodâmos/Rodâmî addatus etic bratûn te
Addatus
Arcimâs
Slanon te
Bratûn te
Molâmos/Molâmî Celtînan
Iâmos/Iâiumî in tancê
Invocation for Celtînâ
We/I invoke Celtînâ
First mother of the Galatîs
First in might and beauty
Valourous in all ways
Great Mother of the Galatîs, pride of the ages, your glory begat us
We/I give offering and thanks to you
Offering
Requests
Cheer to you
Thanks to you
We/I praise you Celtînâ
We/I go in peace
Free Day
Diioi, VII, XIV, XXII, XXIX
Days, 7, 14, 22, 29
(Refer to Toutâdêuoi and Toutâregentiâ)
Carnonos
Diios XV, XXX
Days, 15, 30
Adgarion Carnonû
Adgariomos/Adgariūmī Carnonon
Uernos mantali
Entar bitoues
Agetios Ecuoues
antê trirîgion sesîi etic ages anatiâ
Rodâmos/Rodâmî addatus etic bratûn te
Addatus
Arcimâs
Slanon te
Bratûn te
Molâmos/Molâmî Carnonû
Iâmos/Iâiumî in tancê
Invocation for Carnonos
We/I invoke Carnonos
Warden of the roads
Between worlds
He Who Guides the Herds
At the border of the realms, you sit and guide souls
We/I give offering and thanks to you
Offering
Requests
Cheer to you
Thanks to you
We/I praise you Carnonos
We/I go in peace

